Key Points
-
First Nations and native tribes in the US and Canada are indigenous peoples with rich, diverse cultures and histories, though exact details vary widely.
-
Research suggests there are around 634 recognized First Nations in Canada and 573 federally recognized tribes in the US, with populations of about 1 million and 3.7 million, respectively, based on recent data.
-
It seems likely that historical colonization caused significant population declines and cultural disruptions, with ongoing challenges like health disparities and efforts toward reconciliation.
-
The evidence leans toward diverse cultural practices, including unique languages and traditions, with ongoing efforts to preserve these heritages.
Overview
First Nations and native tribes are the indigenous peoples of Canada and the US, respectively, with deep historical roots and diverse cultural identities. In Canada, First Nations exclude Inuit and Métis, while in the US, they are often called Native Americans or American Indians. Both groups have faced significant historical challenges, but there are ongoing efforts to address these issues and preserve their cultures.
Population and Recognition
-
Canada has 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands, with a population of about 1,048,400 as of 2021 First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia.
-
The US has 573 federally recognized tribal governments, with approximately 3.7 million people identifying as Native American alone in the 2020 census Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
Cultural and Historical Context
-
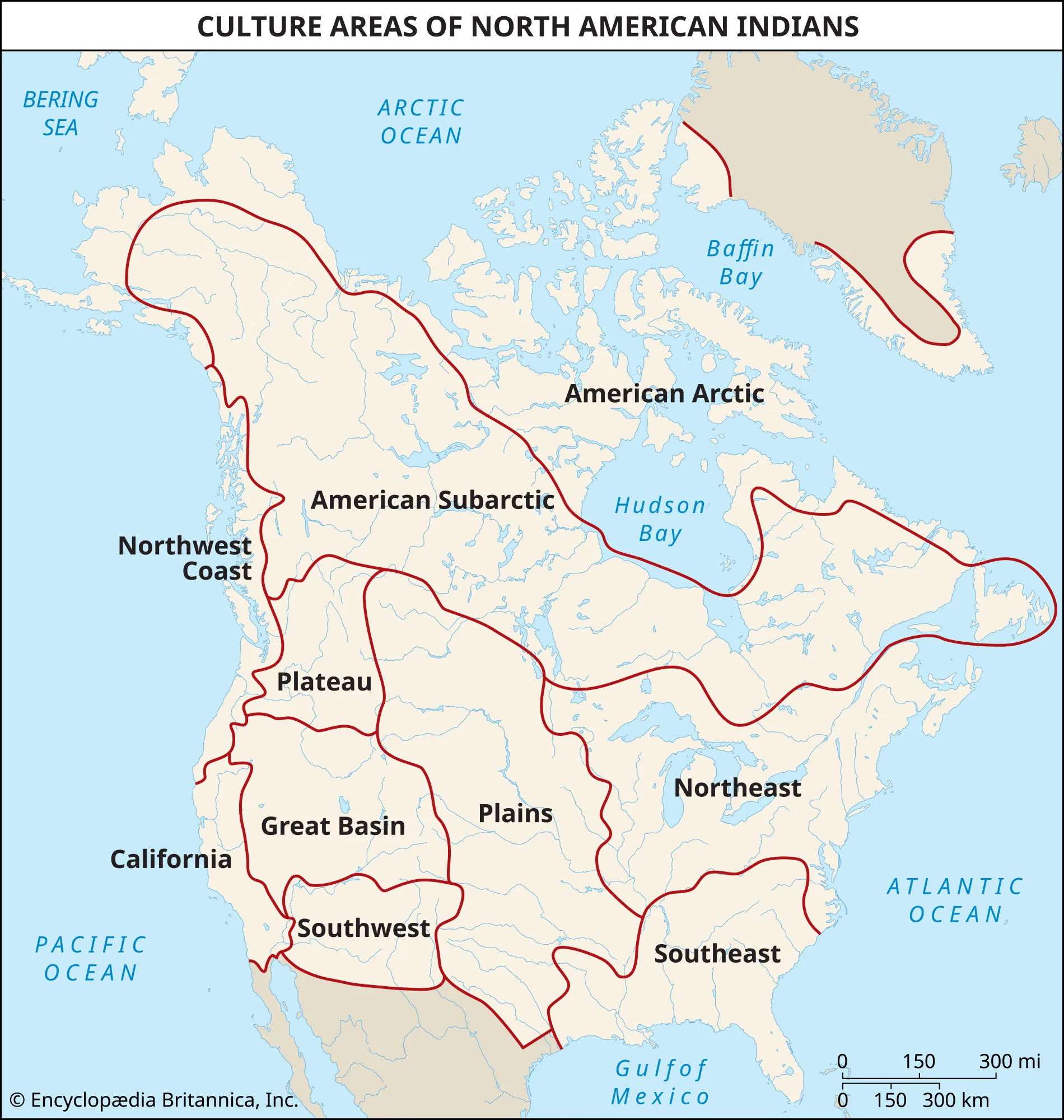
First Nations in Canada are grouped into six geographic areas, such as Woodland and Plains, each with unique social and spiritual practices First Nations in Canada – Government Resource.
-
Native Americans in the US are categorized into cultural areas like Northeast and Southwest, with diverse traditions Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
-
Historical colonization led to population declines due to diseases, conflicts, and land loss, with ongoing efforts for reconciliation and cultural preservation.
Survey Note: Comprehensive Details on First Nations and Native Tribes in US and Canada
This survey note provides an in-depth exploration of First Nations and native tribes in the US and Canada, covering their definitions, demographics, cultural practices, historical contexts, and contemporary issues. The information is derived from a range of authoritative sources, ensuring a comprehensive overview for readers interested in understanding these indigenous communities.
Definitions and Terminology
First Nations and native tribes refer to the indigenous peoples of North America, with specific terminologies reflecting regional contexts. In Canada, “First Nations” is used to describe indigenous peoples excluding Inuit and Métis, a term that gained prominence in the 1980s to replace “Indian band,” driven by activism to avoid offensive language First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. In the US, they are commonly known as Native Americans or American Indians, terms reflecting historical and legal recognition, with preferences varying among communities Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
Under Canadian Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are considered a “designated group” alongside women and visible minorities, though not defined as a visible minority by Statistics Canada First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. In the US, Native Americans are recognized as having origins in any Indigenous peoples of North or South America, maintaining tribal affiliation or community attachment Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
Demographics and Distribution
The demographic profiles of these groups highlight their significance within their respective nations. In Canada, there are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands, with a total population of 1,048,400 as of 2021, accounting for 2.83% of Canada’s population First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. The distribution across provinces and territories is detailed in the following table:
|
Province/Territory
|
2021 Population
|
|---|---|
|
Newfoundland and Labrador
|
28,435
|
|
Prince Edward Island
|
2,165
|
|
Nova Scotia
|
28,050
|
|
New Brunswick
|
20,955
|
|
British Columbia
|
180,085
|
|
Quebec
|
116,555
|
|
Ontario
|
251,030
|
|
Manitoba
|
134,890
|
|
Saskatchewan
|
121,175
|
|
Alberta
|
145,640
|
|
Yukon
|
6,935
|
|
Northwest Territories
|
12,315
|
|
Nunavut
|
180
|
|
Canada Total
|
1,048,400
|
In the US, the 2020 census reported 3,727,135 Native Americans identifying as one race alone, and 5,938,923 in combination, totaling 9,666,058 alone or in combination, representing 2.92% of the US population Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia. Significant populations are found in states like California (631,016) and Oklahoma (332,791) Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
Cultural and Historical Context
Both First Nations and Native Americans have cultures spanning thousands of years, with oral traditions and archaeological evidence providing insights into their histories. In Canada, First Nations are grouped into cultural areas such as Arctic, Subarctic, Northeast Woodlands, Plains, Plateau, based on ancestral lifeways at European contact, corresponding to physical and ecological regions First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. Notable groups include Athapaskan-speaking peoples, Haida, Blackfoot, Cree, and Anishinaabe, with diverse communities established by 500 BCE–1,000 CE First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia.
In the US, Native Americans are classified into ten geographical regions with shared cultural traits, such as the Northwest Coast known for salmon fishing and large villages Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia. Historical records note pre-Columbian population estimates ranging from 2 million to over 18 million, declining to ~600,000 by the end of the 18th century due to diseases, warfare, and genocide Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
European contact, beginning in the late 15th century for Canada and 1492 for the US, led to significant population declines (40–80% in Canada, similar in the US) due to diseases, conflicts, and land dispossession First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia. This period also saw the imposition of legal frameworks, such as the Indian Act of 1876 in Canada and the Indian Appropriations Act of 1871 in the US, affecting land rights and governance First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
Cultural Practices
Cultural practices are integral to the identities of both groups, encompassing languages, art, music, and spiritual beliefs. In Canada, over 30 indigenous languages are spoken, with major ones like Anishinaabe and Cree having up to 150,000 speakers, and efforts to maintain official status in regions like Nunavut (Inuktitut, Inuinnaqtun) and Northwest Territories (11 languages including Chipewyan, Cree, Gwich’in) First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. Art traditions span Northwest Coast, Plateau, Plains, Eastern Woodlands, Subarctic, Arctic, focusing on portability and ceremony, renewed by artists like Mungo Martin and Bill Reid from the 1950s–1960s First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. Music includes social and ceremonial forms, historically suppressed post-European contact First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia.
In the US, major language families include Na-Dené (200,000 speakers, mostly Navajo), Algic (180,000 speakers, mainly Cree, Ojibwe), and Uto-Aztecan (1.95 million speakers, mostly Nahuatl), with efforts like the Cherokee Nation’s 10-year language preservation plan aiming for 80% fluency in 50 years, investing $3 million in schools and curricula Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia. Art industries bring over $1 billion annually, protected by the Indian Arts and Crafts Act of 1990, including pottery, paintings, and jewelry Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia. Music is mostly monophonic, featuring drumming, flutes, and pow-wows with honor and intertribal songs Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
Legal and Political Status
Legal frameworks differ significantly between the two countries. In Canada, the Indian Act of 1876 defines First Nation citizenship and regulates reservations, with the Royal Proclamation of 1763 (Indian Magna Carta) referring to them as tribes or nations First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. The Assembly of First Nations (AFN) represents First Nations, focusing on governance and representation First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. In the US, tribes were initially semi-independent nations, with treaties ending post-1871, treated as “domestic dependent nations” with preserved tribal sovereignty Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia. The Indian Citizenship Act of 1924 granted citizenship, and the Civil Rights Act of 1968 included the Indian Civil Rights Act, applying Bill of Rights guarantees within tribes Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
Contemporary Issues
Both groups face significant contemporary challenges. In Canada, First Nations experience higher rates of unemployment, incarceration (17% of incarcerated in 2007 vs. 2.7% population), substance abuse, health problems, homelessness, fetal alcohol syndrome, lower education, and poverty, with life expectancy 8.1 years shorter for males and 5.5 years shorter for females (2001 data) First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. Suicide rates are more than twice the sex-specific and three times the age-specific rates of non-Aboriginal Canadians, with 400 communities facing water problems between 2004–2014, and 32 systems under long-term boil-water advisories as of October 2021 First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. Missing and murdered Aboriginal women account for 16% of female murder victims and 12% of missing women since 1980, totaling 1,181 cases by 2014 First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia.
In the US, Native Americans face poverty, health disparities (high rates of diabetes, alcoholism, tuberculosis, suicide), societal discrimination, and sexual violence, with 70% living in urban areas as of 2012, up from 45% in 1970 and 8% in 1940 Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia. Economic barriers include lack of access to capital and effective planning, with crime on reservations showing high incidence of rape (1 in 3 Native women, 46% beaten/stalked by intimate partner) Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia. The gambling industry, with 460 operations by 240 tribes in 2011, generated $27 billion in revenue, offering economic opportunities Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
Notable Tribes and Contributions
Notable First Nations in Canada include Cree, Ojibwe (Anishinaabe), Mi’kmaq, Haida, each with distinct cultural practices First Nations in Canada – Wikipedia. In the US, prominent tribes include Cherokee, Navajo, Sioux, Apache, Iroquois, with significant contributions to art, literature, and sports, such as Jim Thorpe’s Olympic achievements and Joy Harjo’s literary works Native Americans in the United States – Wikipedia.
Conclusion
This survey note underscores the complexity and richness of First Nations and native tribes in the US and Canada, highlighting their historical resilience, cultural diversity, and ongoing challenges. Efforts toward reconciliation, cultural preservation, and addressing contemporary issues are crucial for supporting these communities in their continued journey.
Discover more from LEW.AM Asset Management
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.